Malmesbury in the First Civil War – 1642-46
Alan Turton • 31 October 2021
Malmesbury in the First Civil War – 1642-46
By Alan Turton
| Date | Event | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| 1620s – 30s | Malmesbury residents involved in protests against enclosures of the Common Land. They knock down fences and flatten banks. They are called Levellers. | |
| Autumn 1642 | Earl of Pembroke, Lord Lieutenant of the County of Wiltshire raises the Trayned Bands of the County for Parliament in the Boroughs of Malmesbury and Devizes. | |
| 10 January 1643 | Sir Edward Baynton MP for Chippenham is made senior officer for Parliamentary forces raised in Wiltshire. | |
| 11 January 1643 | Baynton evacuates Malmesbury and retreats to Devizes. As a consequence, the burgesses of Malmesbury seek support from Sir Edward Hungerford, who responds by going to Malmesbury to show his support. | |
| Meanwhile Sir Edward Baynton, hearing this sends 140 Dragoons under Captain Eyre pretending to be reinforcements, however in the night, Eyre arrests Hungerford. News of this is carried to the Parliamentary Garrison at Circencester who send three troops of horse to rescue Hungerford. When they get to Malmesbury, Baynton has arrived and they arrest him and release Hungerford. Parliament comes down on Hungerford’s side and on 31 January 1643 Hungerford is made CinC of Wiltshire. | ||
| 2 February 1643 | Price Rupert storms and takes Cirencester. | |
| 3 February 1643 | Hungerford abandons Malmesbury leaving only a few men to defend it. | |
| 4 February 1643 | Malmesbury surrenders to Royalist Lt Col Herbert Lunsford who arrives with 400 foot and a troop of horse. | Malmesbury now garrisoned for the King |
| 22 March 1643 | Parliament’s Major General Sir William Waller attacks Malmesbury at The Bar. | |
| 23 March 1643 | At 0800 hrs Waller enters the town and the Royalists surrender. | |
| 24 March 1643 | Waller leaves Sir Edward Hungerford in charge of the town, however within two days Hungerford flees to Bath leaving a small detachment under Sergeant Major Clifton to hold the town. | |
| 25 March 1643 | Royalists reoccupy the town. Colonel Bampfylde is made governor. | |
| 22 April 1643 | Royalist garrison withdrawn to assist the King’s Oxford army in their unsuccessful attempt to relieve Reading. | |
| 21 July 1643 | Royalists retake Malmesbury in a night attack. Colonel Henry Howard is made governor. | |
| 24 May 1644 | Colonel Edward Massey Parliamentary Commander from Gloucester summons Malmesbury having taken Royalist outposts at Tetbury and Beaverstone Castle. | |
| 25 May 1644 | Massey occupies Malmesbury. | |
| 16 June 1644 | Colonel Nicholas Devereux is appointed governor of Malmesbury. | Nicholas Devereux and his wife Bridget occupy Abbey House |
| 9 May 1645 | Malmesbury threatened by Royalist force but they are driven away. | |
| 30 September 1646 | Parliamentary garrison stood down, town returns to peace. |
[Note: This series of articles was written by Charles Kightly, illustrated by Anthony Barton and first published in Military Modelling Magazine. The series is reproduced here with the kind permission of Charles Kightly and Anthony Barton. Typographical errors have been corrected and comments on the original articles are shown in bold within square brackets.]
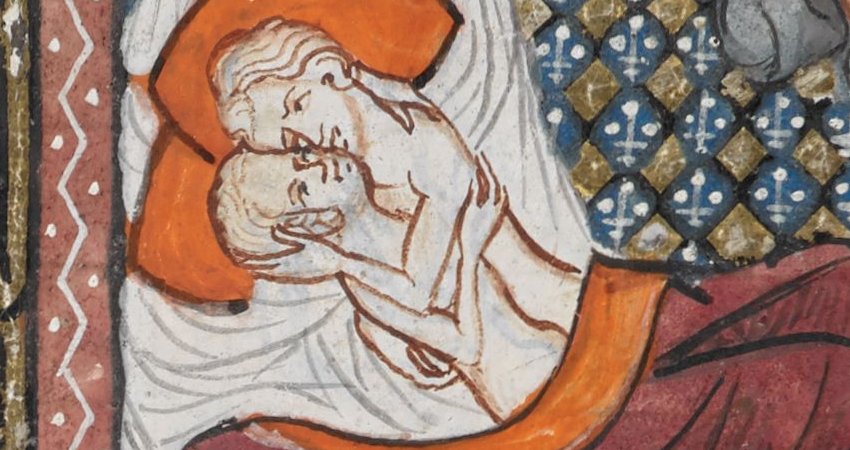
Housekeeping I will be referring to men and women as those people possessing a penis and vagina respectively - there are very few sources I can find for discussing how the medieval people thought about intersex individuals, so I’m just leaving that out. I will also be using both clinical and slang terms for body parts and activities, where appropriate - these terms may be offensive at times, again, I’m trying to reflect the medieval attitude towards men, women and sex. Try to keep sniggering to a minimum. This goes double for Ant. Chapter 1: Who is doing it? The Ladies Women’s status in medieval society is defined by their relationship status, which largely also dictates their sexual status. Women can be: Virgins - not allowed to have sex Wives - allowed to have sex, with certain rules Widows - have had sex before, but not currently allowed to have sex. Whores - allowed to have sex, but socially excluded and vilified Women are only allowed to have sex within a marriage to be respectable - all other women are supposed to be celibate to maintain societal worth. Virgins can be of two types: Virgins by circumstance - young, unmarried women, whose choices are marriage, if they can find a husband, or taking a vow of virginity Virgins by choice - this normally means nuns. It can also mean married or widowed women who have taken a formal vow of chastity before a bishop. Two famous examples of this are Margery Kempe (1373-1438 approx.), who negotiated a ‘chaste marriage’ with her husband after 14 children to devote her life to God, and Margaret Beaufort who took a vow of chastity in 1499 (with her husband’s permission). Contrary to current common wisdom which states that men think about sex every sex seconds...I mean six seconds...in medieval society, everyone knew that women are UP FOR IT. ALL THE TIME. It was thought that not only do women want sex more than men, but that they gain greater pleasure from the act as well. This, coupled with their innate weakness and susceptibility to temptation, leads to a greater need to control their sexual access to prevent sin and bastards overrunning the earth. Women were expected to go to the marriage bed a virgin and to confine their sexual activity to their husband, but ‘wife out to get extracurricular sex’ was an extremely well-worn trope, and prosecutions in court for adultery and fornication were fairly common. Prostitutes held a very particular place in the medieval mindset. Even the great Church fathers St. Augustine and St. Thomas Aquinas recognise that prostitution serves a public good. It wasn’t seen as ironic that the Bishop of Winchester taxed and regulated the sex trade in Southwark in the 15th century. Prostitutes themselves were also seen as a breed apart from respectable women - they were not the lowest of the low - many of the C15th Ordinances are regulations protecting the prostitutes themselves from exploitation by brothel keepers or stewhouses, but there were also rules on public dress for them, so that respectable members of society knew at a glance their profession. The Gents Gents were much less defined by their sexual status, and while it was acknowledged that men should also not be sowing their wild oats too much because it is immoral, the church and court punishments for adultery and fornication for men are less severe in practice. There are celibate men in members of the clergy and men in holy orders, but celibacy for priests is only made canon law in 1123, and this with an emphasis on the ‘unmarried’ meaning of the term; sexual continence was also expected, but it was something that was recognised as difficult. There are court cases of clergy with ‘housekeepers’ who seem to fall pregnant while unmarried a fair amount, and there are increasing urban legends of clerical sexual misconduct as the reformation draws closer, which while probably largely fabricated, was plausible enough to be accepted. Chapter 2: Why are they doing it? Nature Calls Medieval medicine and understanding of biology was based on Ancient Greek and Roman texts, with Galen, Hippocrates and Aristotle having a big influence. The accepted wisdom is that there are four humours in the body, corresponding to four qualities, four elements and four temperaments. Blood, Black Bile, Yellow Bile and Phlegm are in turns Hot, Cold, Dry and Wet. Men are hot and dry - this is optimal. Women, however are cold and wet by nature. When your humours are out of whack, it leads to illness. Men, by virtue of their hotness and dryness, are able to burn off excess and imbalanced humours and thus not be polluted by them, whereas women lack the heat to do so. This leads to both menstruation (explained as the purging of those poisonous excess humours) and to their desire for sex - sex generates the heat they lack and male seed provides heat as well. This is why women are always UP FOR IT. It is also important for men and women to have regular sex as a mechanism to keep their bodily humours in the correct balance.
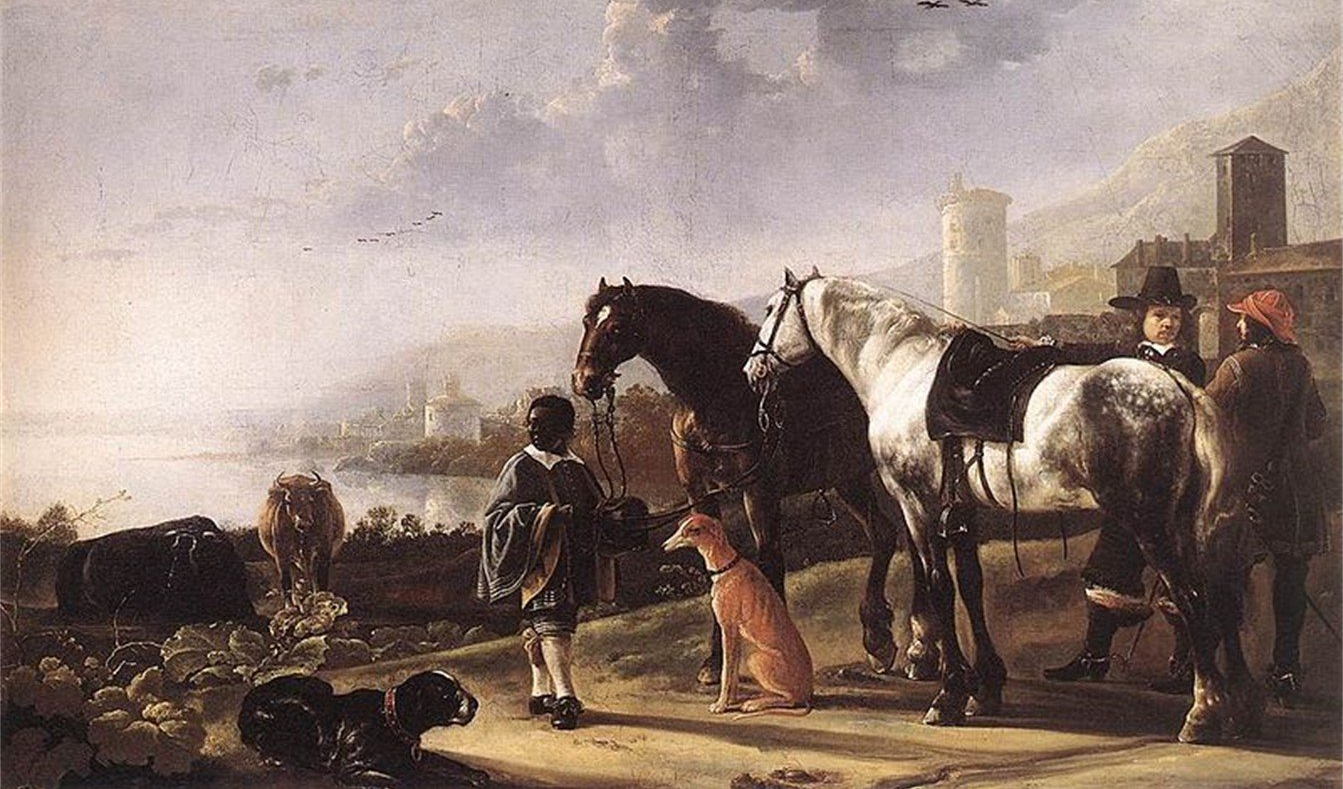

The simple answer to this question is yes; Black People (People of African dependency) had been part of the British landscape for 1500 years when the Civil War broke out. Earliest records of Black people in Britain goes back to 210AD when a Black Roman soldier was described in military records as “this Ethiopian of great frame amongst clowns and good for a laugh”. Later in the 3rd Century up to 500 Roman cavalry originating from Sudan and Ethiopia who were part of the Muarorum Aurelianorum which was named after Emperor Marcus Aurelius who was described as a “Moor”. More evidence of Black troops being part of Roman Britain on Hadrian’s Wall at a fort at Aballava near Burgh by Sands , Carlisle and modern DNA testing of the existing inhabitants shows much higher than average levels of African DNA indicating that they troops mingled with the local indigenous population potentially marrying and having families. Archaeological excavations in Sycamore Terrace, York discovered a 4th Century high status stone coffin containing the remains of the “Ivory Bangle Lady” who was a sub Saharan Black lady about 5 foot tall who died in her early 20’s. She was well nourished and the grave was adorned with high status grave goods. The archaeologists suspected she could have been the wife of a senior military commander or a successful trader. Continued excavations on the site and the subsequent DNA testing of skeleton’s led to an estimate that up to 10% of this important Roman city had their origins in Africa. Not all evidence of Black people in early Britain were directly related to the Roman army, in 1953 the discovery of “Beachy Head Lady” during an excavation of an early Anglo-Saxon cemetery from about 200-245AD that raised in excess of 300 skeleton’s. This one skeleton, during DNA testing, showed that this young woman originated sub-Saharan Africa although brought up and lived for some time in Sussex.

As many of you know, I do medieval (War of the Roses) re-enactment in my spare time and a lot of this takes the form of archery and not just dressing up in lots of tin and battering each other One of the questions that is asked by the public is about the use and effectiveness of the longbow compared with the matchlock. From my personal point of view, I would take a longbow over a musket any day but apart from the illustrations by William Neade’s Double Armed Man project of 1625, I have not seen any real evidence of its use However, I did stumble across an excerpt from a book called “Seventeenth-Century Military Archery” by E.T Fox that provides evidence of significant use and some lovely illustrations. The author explains how as a weapon of war, the longbow began to fall from favour in the sixteenth century, so much so that King Henry VIII had to introduce a number of statutes enforcing the practicing of archery in an attempt to maintain a force of available archers if required. In Queen Elizabeth I reign, the longbow less and less popular until, in 1589, her Privy Council reorganised the trained bands and removed archers from their ranks. With its strong tradition though, the longbow didn’t disappear and its use continued particularly in provincial and rural regions well into the seventeenth century. In Repton, Derbyshire, mustered militia men had “a cote and bowe and a shiffe of arrows and a quiver” in the reign of James I and as late as 1628, Sir Phillip Carteret wrote that Jersey had a force of 3000 able bodied men for the defence of the island, of whom 300 were armed with musket and pikes, “the rest having bows, bills and unarmed” As late as 1638, the Earl of Arundel at Carlisle requested, “some quantity of bows with offensive arrows should be poured into the bordering shires of Cumbria, Northumberland and Westmorland” During the seventeenth century there were a number of schemes to revive the use of the longbow, the best known of which is probably the famous William Neade’s project of 1625 that we all know as the “Double Armed Man”. Neade’s idea was that by arming a pikeman with a longbow in addition to the pike, they would no longer be restricted to standing around on the battlefield getting shot for the majority of the time and waiting just in case they were needed to defend the remaining troops from cavalry. Armed with a longbow they would have an offensive role in addition to their defensive capability.

Key Points... There is occasional evidence for the use of tents by ordinary soldiers, but billeting in existing civilian buildings or purpose built huts was far more common. Tents were normally the preserve of officers during the English Civil War. The use of tents by regular soldiers was much more common during the contemporary wars in Ireland and Scotland. Where tents were used en masse, they seem to have been made to a standard design: 7ft square and 6ft high, to accommodate a file of six soldiers. Introduction... This article is formed of two parts: the evidence for tent use by soldiers during the Civil Wars, and where issued, the form and fabric of such tents. Our focus is on the British Isles during the 1640s and 1650s. Evidence from the continent and from earlier and later eras is incorporated into Part Two, as it helps to inform our overall understanding and acts as bridge across knowledge gaps when we are compelled to make choices in physical reconstruction. Two surviving examples of 17th century tents, from Austria and Switzerland, are used as examples of tent-making techniques. The layout and organisation of camps, or castramentation, is a vast subject by its self, and will not be examined in this article. Mark will be leading a separate debate over the choices we have in portraying a 17th century encampment. Part One: The Nature of Evidence for Tent Usage There is evidence for use of tents by common soldiers during the English Civil War, however it is very limited. There is a comprehensive and objective summary of the available evidence in A.J.Rowland’s “Military Encampments of the English Civil Wars”, published by Stuart Press. I would heartily recommend anyone with an interest in the subject to beg, borrow or steal a copy. Factors in Choosing Shelter. Therefore, the type of overnight shelter available to our generic ECW infantryman would depend upon a series of factors – the tactical activity of the unit, coherent forward planning, the weather, the availability of civilian buildings, time available for setting up the camp, and time in place, availability of timber and thatch, and the immediacy of the threat posed by the adversary. Billeting as the Default Option Suffice to say, it appears that sleeping in billets (requisitioned civilian buildings) was most common, for most soldiers, most of the time. Suitable billeting sites would be planned and reconnoitred in advance. Only on occasion were soldiers forced to sleep outside, under which circumstances hedges, bushes and trees served as overnight shelters. Better Hutting than Tenting. Where time allowed impromptu shelters known as ‘huts ‘were built, but this was dependent on arrival at the campsite early enough for the surrounding countryside to be ransacked for wood and thatching. Despite the time required to build, and resulting impact on local communities, huts appear to have been preferred over tents. When well constructed, they would be more weatherproof than the average tent and when no longer required could simply be burned rather than require transportation. Fig 1: An officer’s tent, with sentinel. Detail from the portrait of Sir Horace Vere (Sir Thomas Fairfax’s father in-law)

This receipt makes 2lb (900g) of marmalade You will need... x 5 Large Lemons or Oranges x 3 Dessert Apples (e.g. Cox’s Pippins) x 150ml Water x 450g Sugar Method... Take a stainless-steel pan Cut the pointed end off the Lemons (take the tops/bottoms off Oranges) and quarter them, removing the pips and put them in the pan. Peel, core and quarter the apples and put them in the pan with the water Cover and simmer for around 45-60 minutes or until tender Remove from the heat and make unto a pulp by either rubbing it through a sieve with the back of a wooden spoon or use a blender – it needs to be smooth Weigh the pulp and transfer it into a clean saucepan with its own weight of sugar Stir over a low heat until it boils to setting point (105˚C/221˚F) This can be used in several ways: To store for a while, pack into sterilised glass jars and sealed as is usual Spoon into small waxed baking cases Or, as I prefer; spread approx. 10mm thick onto a sheet of waxed paper on a baking tray and then cut into cubes, lozenges, sprinkled with caster sugar and guzzled down with an indulgent smile :) Dutch Pudding The word ‘pudding’ conjures up all sorts of sweetness in the mind; Roley Poley, Spotted Dick, Syrup Sponge, Lemon Rice Pudding (a particular favourite of our beloved carb-denier The Dark Lord, aka Spencer Houghton). But who would ever have described a savoury as a ‘pudding’? Our C17th ancestors. The clue is in the name. This is a lovely, cheap showstopper. I served it to the Officers at an event circa 1994 with a simple herb sauce. To be fair; I’ve never heard them Officer types so silent… until the sweet stuffe came to the table. Anyhoo; I digress... You will need... x a good square of muslin, or linen cloth. x 350g Coarsely minced beef x 225g Suet x 100g Dry (Stale) breadcrumbs x 2 tsps Dried sage x 1tsp Dried savory x 1st Dried thyme x 2 Eggs x ¼ tsp Ground cloves x ¼ tsp Ground nutmeg x ¼ tsp Ground mace x ¼ tsp Pepper x 2 tsp Salt x A few lovely White cabbage leaves Method... Aside from the cabbage leaves; mix all ingredients together in a large bowl (by hand; it’s great fun) Form the meaty mix into round ball Wrap the ball completely in cabbage leaves; ensuring there are no gaps Tie the ball of loveliness tight into the cloth. I take a strip from the cloth and use that to make a tie; tying it so as to leave a loop to catch it with when lifting in the pot. Plunge into a large pot of already boiling water (anything less than boiling will automatically spoil any kind of pudding; sweet or savoury) Simmer for 2 hours Serve on a bed of fresh breadcrumbs or ‘sippets’ (cubes of bread; toasted or not) It looks just like cabbage; until cut VOILA!




